
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure performed through very small incisions in the abdomen, using specialised instruments. The abdominal cavity is inflated with carbon dioxide gas (CO2) and distended. A pencil-thin instrument called a laparoscope is used; it has lenses like a telescope to magnify body structures, a powerful light to illuminate them, and a miniature video camera. The camera sends images of the inside of the body to a TV monitor in the operating room. Specialised surgical instruments can be inserted through the small incisions nearby. This type of surgery is called "minimal access" because of the very small incisions used. Yet major procedures can now be performed using this technique.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is used to look inside the uterus. If an abnormal condition is detected during the diagnostic procedure, operative hysteroscopy can often be performed to correct it at the same time, avoiding the need for a second surgery.
Laparoscopy is easier on the patient because it uses a few very small incisions. For example, traditional "open surgery" on the abdomen usually requires a ten to fifteen centimetre incision through layers of skin and muscle. In laparoscopic surgery, the doctor usually makes two to three incisions that are less than a centimetre long.
The smaller incisions cause less damage to body tissue, organs, and muscles so that the patient can go home sooner after a shorter hospital stay Recovers quickly and returns to work and their normal routine earlier. In contrast, traditional laparotomy may require a person to limit daily activities for four to eight weeks. Experiences fewer post-operative complications and less pain. Has less scaring. Laparoscopy for diagnosis and treatment Laparoscopy can be used either to diagnose or to treat various conditions. Or it may be used to identify a problem and treat it in the same operation.
Diagnostic laparoscopy allows the doctor to look at structures inside the abdomen and see whether they appear normal or abnormal. It becomes valuable when physical examinations, lab tests and scans don't show exactly what is wrong and a diagnosis requires a direct look inside the body. It can be used to diagnose the cause of pelvic pain, infertility and to perform a biopsy. Laparoscopy can be used to determine the stage of certain kinds of cancer. Stage means how far the cancer has advanced. Operative laparoscopy allows the doctor to treat a disease or condition. It usually involves removing diseased tissue or repairing damage to a structure in the abdomen.
Dozens of different kinds of operations are now being done using these new minimally invasive techniques. Gynecological conditions or procedures which can be performed endoscopically include:
Yes, even a very large uterus or large fibroids can be removed laparoscopically. The tissue to be removed is cut into pieces with specially designed- for this purpose-instruments. Then the pieces are removed through one of the incisions.
Since laparoscopy involves minimal damage to body tissues, it is generally safer than open operations. A complication is an unforeseen problem that occurs during or after surgery, such as internal bleeding or injury to a healthy organ.
Risks for any type of surgery may be greater for people who are obese or have additional medical problems Laparoscopy usually requires general anesthesia, which carries certain risks. Modern general anesthesia, however, is safe and reactions are rare. Injury to blood vessels or organs, which causes bleeding are possible complications. Sometimes the surgery cannot be successfully completed by laparoscopy. Then the doctor may have to complete the operation using traditional "open" abdominal surgery, called laparotomy. This is called "converting" to laparotomy.
It takes special training to do laparoscopic surgery. Patients may get traditional "open" surgery because that is the only kind their doctor offers. Doctors need to perform laparoscopy regularly in order to develop and maintain their skills.
Since laparoscopy involves minimal damage to body tissues, it is generally safer than open operations. A complication is an unforeseen problem that occurs during or after surgery, such as internal bleeding or injury to a healthy organ.
For laparoscopy, the patient is usually given a general anesthesia and is unconscious during the operation. General anesthesia relaxes muscles and makes it easier for the doctor to perform the surgery. Some procedures however are done with a local anesthetic.
Individuals scheduled for laparoscopy usually visit the hospital before the operation for preoperative evaluation and to discuss the procedure in detail. Tests may be ordered, which include blood and urine tests, an electrocardiogram, an ultrasound scan and a x-ray.
Since laparoscopy involves minimal damage to body tissues, it is generally safer than open operations. A complication is an unforeseen problem that occurs during or after surgery, such as internal bleeding or injury to a healthy organ.
Diagnostic laparoscopy usually takes less than half an hour. If the procedure is for treatment, it will depend on the condition and the complexity of the operation. It may take an hour or more and sometimes much longer, depending on the procedure.
The effects of general anesthesia make most people feel groggy at first, but they quickly become more alert. Some people experience nausea for a short time after awakening from a general anesthesia. In the recovery room, the individual first rests in bed, then gradually sits up, stands, and walks as balance and mobility are regained.
Since laparoscopy involves minimal damage to body tissues, it is generally safer than open operations. A complication is an unforeseen problem that occurs during or after surgery, such as internal bleeding or injury to a healthy organ.
Complications after laparoscopic surgery are rare. Most people recover quickly and resume their normal activities without problems. However, the risk of infection or other problems exists as with any kind of surgery. There may be some soreness near the incisions, especially when twisting or stretching the body. If a breathing tube was used for the surgery, patients may have a mild sore throat.
There may be discomfort in the abdomen, upper chest, shoulders, and neck area due to the carbon dioxide used to inflate the abdomen, but this disappears quickly.
Laparoscopic surgeries offered:
Evaluation of uterine cavity is necessary when abnormal bleeding occurs or when the fertility is being evaluated. Hysteroscopic surgeries are performed for these conditions inside the uterus without scarring your body.
Offered Surgeries:
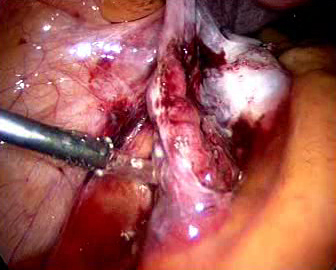
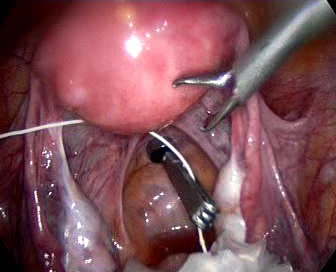
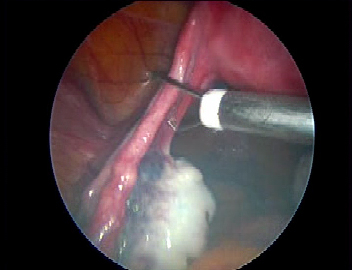
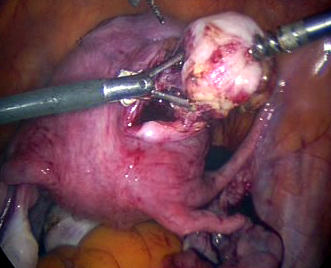
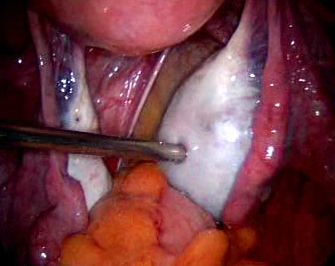
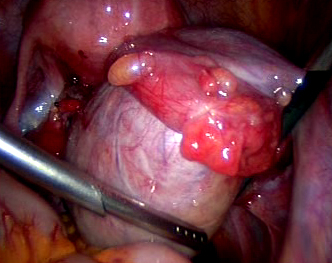
Abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic adhesions, pelvic pain , prolapse of uterus , ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, fibroids, hysterectomy, infertility, ovarian cyst, uterine anomalies etc can be treated with the help of laparoscopic surgery.
Reduced blood loss reduces the chance of blood transfusion. The smaller incision reduces the pain and recovery time and although the procedures are longer hospital stay is less and thereby reduces the expense.
Yes, by all means. Infact more patients are opting for laparoscopic surgeries.
Laparoscopic surgery is also called minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery. It is a modern surgical technique in which operations are performed through small incisions. The key element in this surgery is the use of laparoscope. There are 2 types of lens system that is usually connected to a video camera. Laparoscopic surgery is also called minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery. It is a modern surgical technique in which operations are performed through small incisions. The key element in this surgery is the use of laparoscope. There are 2 types of lens system that is usually connected to a video camera.